Top Strategies MSPs Use to Maintain HIPAA Compliance
- Read more
With the increasing frequency of cyberattacks in the healthcare industry, ensuring HIPAA compliance is more crucial than ever. In January 2023 alone, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office for Civil Rights investigated 30 breach cases involving healthcare providers. This highlights the urgent need for stringent cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient information.
Why Healthcare Providers Are Prime Targets for Cybercriminals
Healthcare organizations are prime targets for cybercriminals due to the valuable data they hold. This includes patients’ personally identifiable information (PII), health records, financial details, and intellectual property like research data. The high value of this data on the black market incentivizes cybercriminals to continuously seek new ways to breach healthcare systems, making robust security measures essential.
Key Practices for Meeting HIPAA Requirements
User and Device Management
Users and devices are often the weakest links in cybersecurity. Effective management of these elements is crucial in maintaining compliance and ensuring the security of sensitive information.
Modern Device Management (MDM)
Modern Device Management allows healthcare organizations to oversee and control all devices within their network, ensuring they are secure, compliant, and optimized.
Key aspects of MDM include:
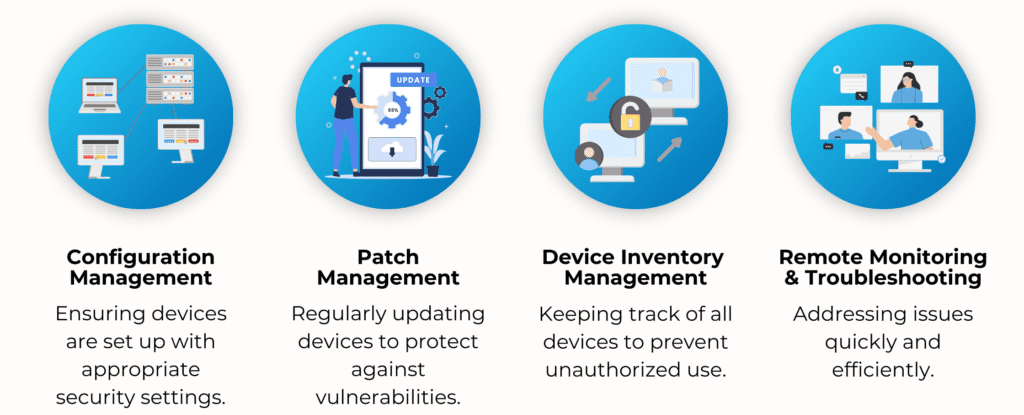
Effective device management prevents unauthorized access, enforces security policies, and minimizes risks, allowing healthcare staff to focus on patient care without compromising security.
Device Lifecycle Services
Mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, are convenient for clinicians and hospital staff but pose significant security risks if lost or stolen. Device Lifecycle Services cover the entire lifespan of a device, from acquisition to disposal, ensuring accountability and security.
Key stages include:
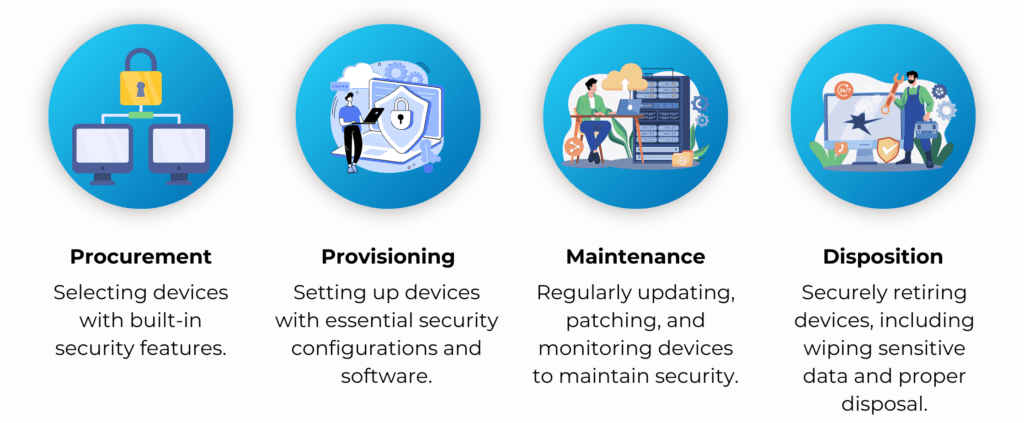
MSPs provide comprehensive Device Lifecycle Services with a single chain of custody, ensuring compliance with HIPAA and peace of mind for healthcare organizations.
Implementing a Zero Trust Framework
Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no implicit trust for any user or device, even those within the network. It operates on the principle that breaches are inevitable and takes a proactive approach to minimize risks.
Key principles of Zero Trust include:
Least Privilege Access: Granting users and devices only the permissions they need.
Micro-Segmentation: Dividing the network into isolated segments to limit the spread of breaches.
Continuous Authentication and Authorization: Regularly verifying user and device identities for every interaction.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is an essential component of Zero Trust, requiring multiple forms of verification (such as a password and a one-time PIN or biometrics) to access resources. This enhances security by combining something the user knows (a password) with something they have (a smartphone).
Comprehensive Cybersecurity Training
Human error is a significant vulnerability in any cybersecurity system. A robust cyber-resilience strategy should include organization-wide training and compliance to prevent and recover from data breaches. This involves:
Regular Training Sessions: Educating staff on the latest cybersecurity threats and best practices.
Simulated Phishing Attacks: Testing staff responses to phishing attempts to identify vulnerabilities.
Clear Policies and Procedures: Establishing and enforcing guidelines for handling sensitive information.
Partnering with a Reliable MSP
Staying ahead of constant cybersecurity threats can be overwhelming for an internal IT team. Partnering with a Managed Service Provider (MSP) can provide the expertise and resources needed to maintain a strong cybersecurity posture.
MSP Services for HIPAA Compliance
MSPs offer a wide range of services, including professional IT services and staffing, to help healthcare organizations streamline and reduce costs. These services include:
Security Risk Assessments: Identifying vulnerabilities and implementing measures to address them.
Compliance Monitoring: Regularly reviewing systems to ensure they meet HIPAA standards.
Incident Response Planning: Developing and implementing plans to respond to data breaches effectively.
Data Encryption: Ensuring that sensitive data is encrypted both in transit and at rest.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Implementing robust backup solutions to ensure data can be quickly restored in case of a breach.
During these challenging times for healthcare, an MSP can be a crucial ally in improving cybersecurity, optimizing patient experience, and achieving IT efficiency. Their expertise ensures that healthcare organizations can focus on their primary mission – serving patients’ needs.
For more information on how MSPs can help your business meet HIPAA standards, read our 10 Essential Ways MSPs Ensure Your Practice Stays HIPAA Compliant

