MSPs Top Strategies to HIPAA Compliance

The Rising Importance of HIPAA Compliance in a Cyber-Threatened Healthcare Landscape
In today’s increasingly digital healthcare environment, the need to safeguard sensitive patient information has never been more urgent. The surge in cyberattacks targeting healthcare organizations over the past several years has transformed HIPAA compliance from a regulatory necessity into a frontline defense against data breaches, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was designed to protect the privacy and security of patients’ health information. While compliance has always been important, the rising frequency and sophistication of cyber threats have elevated its role to a critical component of every healthcare provider’s risk management strategy. HIPAA compliance is no longer just a box to check, it’s an essential part of protecting the integrity and trustworthiness of your practice.
The scale of the threat is significant. In January 2023 alone, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) launched investigations into 30 breach cases involving healthcare providers. These breaches impacted thousands of patients and involved the exposure or theft of protected health information (PHI). While some breaches were the result of internal mishandling, the vast majority stemmed from external cyberattacks, such as ransomware and phishing.
These incidents underscore a harsh reality: healthcare organizations are prime targets for cybercriminals. Why? Because PHI is incredibly valuable on the dark web. Far more than financial data. A stolen health record can fetch hundreds of dollars and be used in a range of fraudulent activities, including identity theft, insurance fraud, and even prescription drug scams.
Unfortunately, many healthcare providers, especially smaller practices, are underprepared to defend against these threats. Limited budgets, outdated systems, and a lack of in-house cybersecurity expertise make them easy targets. In many cases, providers mistakenly assume that their electronic health record (EHR) system or IT vendor handles all aspects of HIPAA compliance. However, true compliance requires a comprehensive, proactive approach that includes everything from secure communication and data encryption to employee training and breach response planning.
The consequences of non-compliance can be severe. Beyond the immediate cost of recovering from a cyberattack, providers face potential fines from the HHS OCR, class-action lawsuits, loss of patient trust, and long-term reputational damage. In some cases, the fallout is so severe that practices are forced to shut down entirely.
To stay ahead of the threat, healthcare providers must prioritize HIPAA compliance as a strategic initiative, not just a regulatory burden. This includes conducting regular risk assessments, updating policies and procedures, securing digital infrastructure, and training all employees on data privacy best practices. It also means partnering with trusted IT professionals who specialize in HIPAA-compliant cybersecurity solutions tailored to the unique needs of the healthcare industry.
In an era where cyberattacks are not a matter of if but when, taking action now is the only way to protect your patients, your practice, and your peace of mind. The data speaks for itself: HIPAA compliance is no longer optional, it’s essential for survival in today’s healthcare landscape.
Why Healthcare Providers Are Prime Targets for Cybercriminals
In recent years, healthcare providers have become some of the most frequently targeted entities in the world of cybercrime. The reason is simple: the data healthcare organizations manage is incredibly valuable, both to the business and to those looking to exploit it.
Unlike other industries, healthcare providers store vast amounts of sensitive and diverse information. This includes personally identifiable information (PII) like names, addresses, birth dates, and Social Security numbers, as well as protected health information (PHI) such as diagnoses, prescriptions, and treatment histories. In many cases, this data is stored alongside financial details, including insurance information and billing records. Together, this comprehensive data set provides cybercriminals with everything they need to commit identity theft, insurance fraud, and even blackmail.
Additionally, healthcare organizations often possess intellectual property, especially those involved in clinical trials, pharmaceutical research, or specialized medical innovations. This type of data is highly sought after not only by criminal groups but also by state-sponsored actors looking to gain a competitive edge.
The black market value of healthcare data is significantly higher than other types of stolen information. While a stolen credit card number might fetch a few dollars, a complete medical record can be worth hundreds. This creates a strong financial incentive for cybercriminals to continually develop more sophisticated methods to breach healthcare systems.
Unfortunately, many healthcare providers remain underprepared for the intensity of these attacks. Limited IT budgets, reliance on outdated software, and a lack of cybersecurity training make these organizations vulnerable. Additionally, the urgency of healthcare services often means security takes a back seat to operational continuity, leaving critical systems exposed.
Threat actors are well aware of these weaknesses. They exploit them through phishing emails, ransomware attacks, and by targeting unsecured medical devices and third-party vendors. Once inside, they can lock down entire networks, steal sensitive data, and demand hefty ransoms knowing that the cost of downtime in healthcare can be life-threatening, not just financially damaging.
To counter this growing threat, healthcare providers must prioritize cybersecurity as part of their patient care mission. Protecting patient data isn’t just about compliance, it’s about trust, safety, and the resilience of the entire healthcare system.
Key Practices for Meeting HIPAA Requirements
User and Device Management: Closing the Gaps in Healthcare Cybersecurity
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, users and devices often represent the most vulnerable entry points into a healthcare network. While sophisticated security systems and software play a critical role in defense, effective user and device management is essential for ensuring HIPAA compliance and protecting sensitive patient data from unauthorized access or breaches.
Healthcare environments typically involve a high volume of users, including doctors, nurses, administrative staff, and third-party vendors, accessing systems across multiple devices. These devices may include desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and even medical equipment that is connected to the network. Without proper controls in place, each user and device expands the attack surface and increases the risk of a breach.
One common vulnerability is inadequate access control. Not every user needs access to all systems or data. By implementing role-based access, healthcare organizations can ensure that staff members can only access the information necessary for their roles. This limits unnecessary exposure and minimizes the impact if a user’s credentials are compromised.
Equally important is device management. All endpoints that access sensitive data must be properly secured. This includes installing antivirus software, enabling encryption, applying software updates, and monitoring for unusual activity. Organizations should also implement mobile device management (MDM) tools to enforce security policies on smartphones and tablets, particularly in environments where bring-your-own-device (BYOD) practices are allowed.
User training is another key component. Many breaches stem from human error, such as clicking on phishing links or using weak passwords. Regular cybersecurity awareness training helps users recognize threats and respond appropriately.
Finally, enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for both users and administrators adds a powerful layer of protection by requiring more than just a password to access systems.
By proactively managing users and devices, healthcare providers can significantly reduce vulnerabilities, strengthen compliance, and maintain the confidentiality and integrity of protected health information (PHI).
Modern Device Management (MDM): Enabling Secure and Compliant Healthcare Environments
In today’s digitally connected healthcare environment, managing the growing number of devices accessing sensitive patient data has become a critical security challenge. Modern Device Management (MDM) solutions provide healthcare organizations with the tools they need to oversee, control, and secure every device within their network. Whether it’s a desktop in an office, a tablet at a patient’s bedside, or a mobile phone used by remote staff.
MDM platforms allow IT teams to centrally manage and enforce policies across all endpoints, ensuring that every device connected to the network meets strict security and compliance requirements. This is especially important in healthcare settings, where data privacy laws like HIPAA mandate rigorous protection of protected health information (PHI).
With an effective MDM solution in place, administrators can:
- Remotely monitor and update devices
- Enforce encryption and passcode requirements
- Restrict access to unauthorized apps or data
- Wipe or lock lost or stolen devices
- Ensure operating systems and apps stay up to date
This level of control significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, data leakage, or compromised endpoints. Three of the most common contributors to healthcare data breaches.
MDM is especially valuable in environments where Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies are allowed. While personal devices offer convenience and flexibility, they also introduce security risks if not properly managed. MDM allows organizations to segment business data from personal data, ensuring sensitive information remains protected without infringing on user privacy.
Modern Device Management also plays a key role in operational efficiency. By streamlining updates, patch deployment, and inventory tracking, MDM reduces IT workload and downtime, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care.
In summary, implementing a robust MDM strategy is no longer optional, it’s essential for any healthcare organization that wants to stay compliant, secure, and agile in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Key aspects of MDM include:
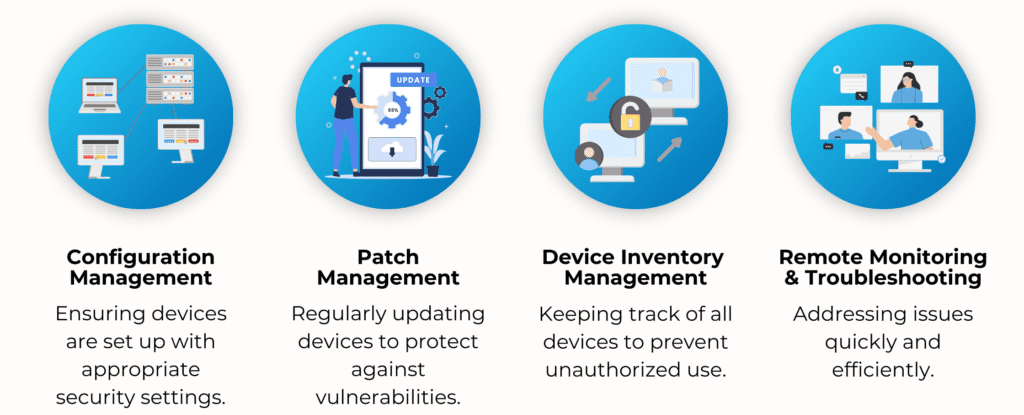
Effective device management prevents unauthorized access, enforces security policies, and minimizes risks, allowing healthcare staff to focus on patient care without compromising security.
Device Lifecycle Services: Securing Mobile Devices from Start to Finish
In today’s healthcare environments, mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops have become indispensable tools for clinicians, nurses, and administrative staff. They enhance communication, streamline access to patient data, and improve workflow efficiency. However, these benefits come with a critical downside, which is increased security risk. If a device is lost, stolen, or improperly disposed of, it can lead to serious data breaches involving protected health information (PHI).
That’s where Device Lifecycle Services (DLS) come into play. DLS is a comprehensive approach to managing mobile and connected devices throughout their entire lifespan. From initial procurement and configuration to regular maintenance, secure decommissioning, and responsible disposal.
Effective Device Lifecycle Services ensure:
- Proper configuration and enrollment into secure management systems upon acquisition
- Ongoing updates and compliance checks to meet HIPAA and internal security policies
- Real-time tracking of device location and usage for full accountability
- Incident response capabilities, such as remote lock and data wipe in case of loss or theft
- Secure decommissioning processes to ensure no data is left behind when a device is retired
In busy healthcare settings, devices are frequently shared, moved, or replaced. Without lifecycle oversight, it becomes difficult to know who last used a device, whether it has the latest security patches, or if it still has access to critical systems. This lack of visibility is a serious vulnerability.
DLS also supports audit readiness by maintaining a complete record of each device’s history, including who used it, when it was serviced, and how it was disposed of. This level of documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance with data protection regulations.
By integrating Device Lifecycle Services into your broader IT and security strategy, your organization can reduce risks, optimize device performance, and ensure that every mobile endpoint is accountable, secure, and HIPAA-compliant no matter where it goes.
Key stages include:
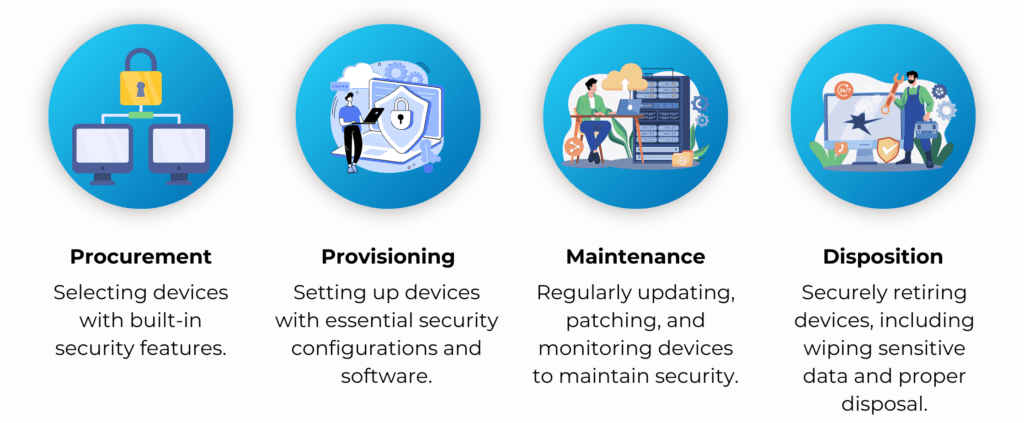
MSPs provide comprehensive Device Lifecycle Services with a single chain of custody, ensuring compliance with HIPAA and peace of mind for healthcare organizations.
Implementing a Zero Trust Framework: Proactive Defense for Modern Healthcare Security
As cyber threats become more sophisticated and persistent, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient especially in highly sensitive sectors like healthcare. Enter the Zero Trust security framework, a modern approach designed to eliminate implicit trust and continuously validate every access request, regardless of where it originates.
Unlike older security models that assume everything inside a network is safe, Zero Trust assumes breaches are inevitable and works to limit their impact. This proactive strategy is especially critical in environments where protecting Protected Health Information (PHI) and ensuring HIPAA compliance are top priorities.
Core Principles of Zero Trust:
- Least Privilege Access
Zero Trust enforces the concept of least privilege, which means users and devices are granted only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks. This minimizes exposure if credentials are compromised and reduces the potential damage from insider threats or lateral movement within the network. - Micro-Segmentation
By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, micro-segmentation helps contain breaches and prevent them from spreading across systems. For example, even if an attacker gains access to one part of the network, they cannot easily move into EHR systems, billing platforms, or connected medical devices without additional verification. - Continuous Authentication and Authorization
In a Zero Trust environment, identity verification isn’t a one-time event. Users and devices are continuously authenticated. Each access request is evaluated in real time based on context, such as location, device health, and usage patterns. - Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
A foundational element of Zero Trust, MFA requires multiple forms of verification before granting access. For instance, a clinician might log in with a password (something they know) and then confirm access via a one-time code sent to their smartphone (something they have), or a biometric scan (something they are). This layered defense makes it exponentially harder for attackers to infiltrate systems using stolen credentials alone.
Implementing a Zero Trust architecture is not a one-size-fits-all solution, it requires careful planning, technology alignment, and user education. But for healthcare organizations committed to security, compliance, and patient trust, Zero Trust offers a powerful, modern approach to reducing risk and enhancing resilience.
Comprehensive Cybersecurity Training: Empowering Your Frontline Defenders
In the realm of cybersecurity, technology alone isn’t enough, people play a critical role. In fact, human error remains one of the leading causes of data breaches in healthcare. Clicking on malicious links, falling for phishing emails, or mishandling sensitive information can open the door to devastating attacks. That’s why comprehensive cybersecurity training is an essential pillar of any effective cyber-resilience strategy.
A successful training program should go beyond one-time onboarding sessions. It must be ongoing, organization-wide, and tailored to evolving threats. Here’s what it should include:
- Regular Training Sessions
Employees at all levels should receive consistent education on cybersecurity best practices, including how to identify phishing emails, create strong passwords, and securely access digital systems. As threats evolve, so should the training content. - Simulated Phishing Attacks
Testing is as important as teaching. Simulated phishing attacks allow IT teams to evaluate how staff respond to real-world scenarios. This helps identify knowledge gaps and provides opportunities for corrective training before an actual breach occurs. - Clear Policies and Procedures
Education must be paired with clearly defined policies. Staff should know exactly how to handle protected health information (PHI), report suspicious activity, and respond during a security incident. Written procedures reinforce expectations and support compliance with HIPAA and other regulations.
By creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness, healthcare organizations can turn their employees into proactive defenders rather than potential liabilities.
Partnering with a Reliable MSP: Extending Your Cybersecurity Capabilities
While internal IT teams are vital, the increasing complexity of modern cyber threats can be overwhelming especially for small to mid-sized healthcare organizations with limited resources. This is where partnering with a Managed Service Provider (MSP) becomes invaluable.
A trusted MSP, like Ekim IT Solutions, offers access to specialized expertise, 24/7 monitoring, and cutting-edge technologies that may be out of reach for in-house teams alone. From managing endpoint security and patching systems to overseeing compliance and incident response, MSPs deliver comprehensive support tailored to your organization’s needs.
Most importantly, an MSP serves as a strategic partner, helping you align IT operations with business goals while continuously strengthening your cybersecurity posture.
In an era where breaches are inevitable, having the right training and the right partner can make all the difference in staying protected and resilient.
MSP Services for HIPAA Compliance
Managed Service Providers (MSPs) play a critical role in helping healthcare organizations maintain HIPAA compliance while improving cybersecurity and IT efficiency. By offering a wide range of specialized services, MSPs allow providers to focus on delivering quality patient care.
Key services include:
- Security Risk Assessments to identify and address system vulnerabilities
- Compliance Monitoring to ensure continuous adherence to HIPAA standards
- Incident Response Planning for swift, effective data breach management
- Data Encryption to protect PHI in transit and at rest
- Backup and Disaster Recovery to ensure data can be restored quickly during outages or cyberattacks
MSPs also provide professional IT services and staffing, helping reduce costs while expanding capabilities. In an increasingly complex threat landscape, partnering with an MSP ensures healthcare providers have the tools, expertise, and support needed to safeguard patient data and stay compliant while focusing on what matters most: patient care.
Ready to Strengthen HIPAA Compliance with Expert Support?
Navigating the complexities of HIPAA compliance can be overwhelming, especially for healthcare practices juggling patient care, technology, and evolving cyber threats. That’s where a trusted Managed Service Provider (MSP) becomes invaluable. From security risk assessments and data encryption to compliance monitoring and breach response, MSPs deliver the tools and expertise needed to ensure your systems are secure, efficient, and compliant.
By partnering with an MSP, you can reduce IT burden, enhance data protection, and focus more fully on your patients while staying confidently aligned with HIPAA requirements.
🗓️ Book a call with us
📞 207-333-2206
📧 info@ekimit.com
🌐 www.ekimit.com
Or check out our free resource:
👉 Your Security Compliance Checklist



